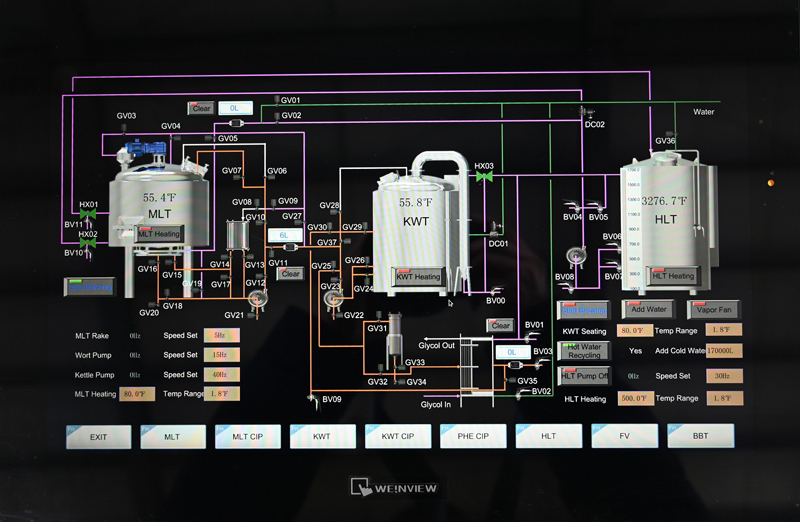
Brewery Cellar Control Panel: What You Need to Know
1. Definition & Purpose
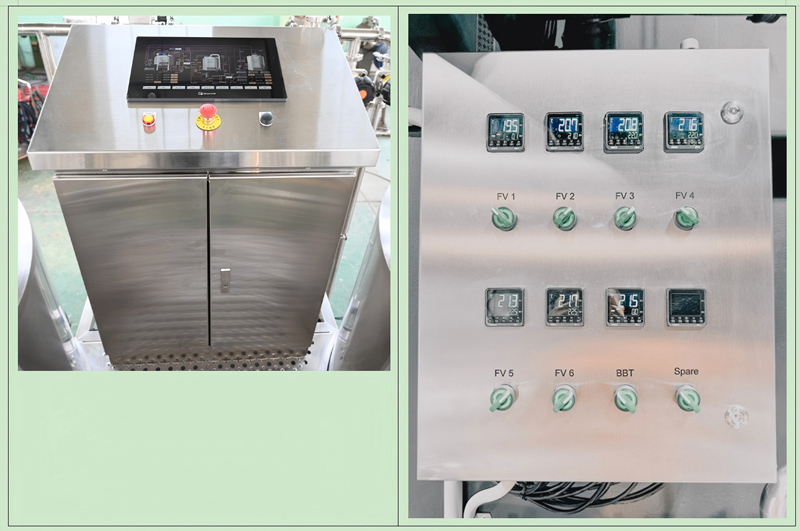
A Brewery Cellar Control Panel is a centralized interface used to monitor and regulate equipment in the fermentation and lagering areas of a brewery. It ensures precise control over critical processes, maintaining product consistency and operational efficiency.
2. Key Components & Functions
2.1 Temperature Control
》Sensors & Actuators: Monitor tank temperatures and adjust glycol cooling systems automatically.
》Zoning: Manage multiple tanks with independent temperature profiles for different beer styles.
2.2 Flow and Transfer Management
》Pumps/Valves: Automate transfers between tanks, kegs, or bright beer tanks.
》Pressure Monitoring: Prevent over-pressurization in fermenters or brite tanks.
2.3 Fermentation Tracking
》Gravity/Pressure Sensors: Track specific gravity (via tilt sensors or refractometers) and CO₂ levels.
》Automated Dosing: Add yeast, nutrients, or finings at scheduled intervals.
2.4 Safety Systems
》Alarms & Emergency Stops: Trigger alerts for leaks, temperature spikes, or pressure failures.
》Sanitization Cycles: Automate CIP (Clean-in-Place) processes for tanks and lines.
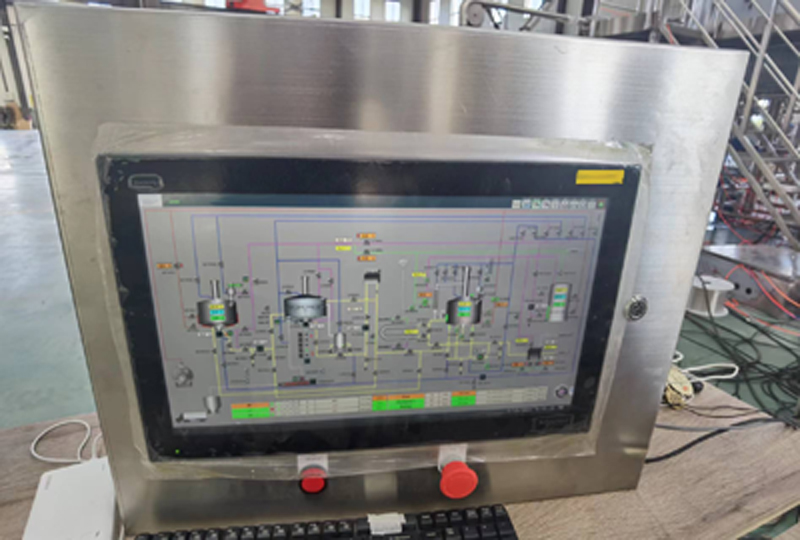
2.5 User Interface
》Touchscreen/PLC: Customizable dashboards for real-time data and manual overrides.
》Remote Access: Control operations via mobile/web apps (e.g., IoT-enabled systems).
2.6 Data Integration
》Logging & Reporting: Record batch data for compliance and quality analysis.
》SCADA/MES Integration: Sync with brewery management software for end-to-end tracking.
3. Importance in Brewing
》Consistency: Ensures repeatability in fermentation, critical for brand integrity.
》Efficiency: Reduces manual labor and energy use (e.g., optimized glycol cycles).
》Safety: Mitigates risks of contamination, equipment damage, or hazardous incidents.
》Scalability: Modular designs allow expansion as production grows.
4. Selection Considerations
》Brewery Size: Match panel capacity to tank volume and cellar complexity.
》Customization: Opt for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to adapt to unique workflows.
》Ease of Use: Prioritize intuitive interfaces for staff training and troubleshooting.
》Vendor Support: Ensure access to technical assistance and software updates.
5. Maintenance Best Practices
》Regular Calibration: Check sensors (temperature, pressure) quarterly.
》Software Updates: Keep firmware/security patches current to prevent vulnerabilities.
》Component Inspections: Clean electrical contacts and test emergency stops annually.
6. Future Trends
》IoT & AI: Predictive maintenance alerts and adaptive fermentation algorithms.
》Energy Optimization: Smart grids integrating renewable energy sources.
》Blockchain Traceability: Immutable batch records for transparency.
Example Use Case
A craft brewery uses the panel to automate a Belgian Saison fermentation:
》Temp starts at 68°F, rising to 80°F over 5 days (controlled via glycol valves).
》Alerts notify staff when final gravity hits 1.008, prompting a transfer to brite tanks.
》Data logs confirm compliance with local alcohol-by-volume (ABV) regulations.
By integrating a cellar control panel, breweries enhance quality, safety, and scalability while reducing operational costs. Always partner with reputable automation specialists for tailored solutions.
Post time: Feb-22-2025